The humanitarian coordinator opens the video conference from Nairobi headquarters. Three thousand field workers across twelve African countries should be joining for critical operational briefing. Five minutes in, participant count drops from 2,800 to 1,200. Chat fills with “can’t hear audio” and “video frozen.” The platform optimized for Silicon Valley networks fails spectacularly on 3G mobile connections in rural Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania.
This scenario repeats daily across NGOs, government agencies, development organizations, and humanitarian operations working in regions where connectivity is constraint, not convenience.
Africa. South Asia. Pacific Islands. Remote conflict zones. Rural communities. Regions where:
- 2G/3G networks remain primary connectivity
- Shared community bandwidth creates congestion
- Satellite links carry 800ms+ latency
- Power instability affects mobile infrastructure
- Urban slums share overloaded networks
Millions of participants in these regions need reliable access to large-scale meetings for:
- Emergency coordination during disasters
- Health campaign training across provinces
- Agricultural extension education
- Election observer briefings
- Development program coordination
- Humanitarian response planning
Standard webinar platforms fail because they assume high-bandwidth, stable networks. Design decisions prioritizing HD video quality over connection reliability. Architecture routing traffic through distant data centers. Heavy client-side processing overwhelming low-power devices.
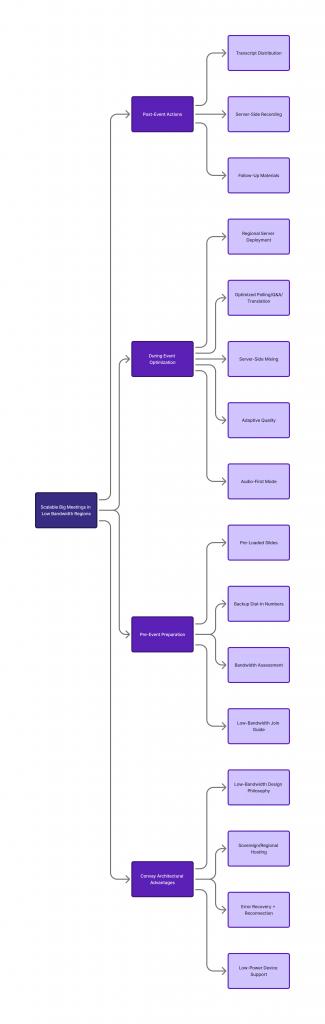
This guide provides technical framework for organizations running 1,000-10,000 participant meetings in challenging connectivity environments. Not aspirational “best practices”—actual architectural requirements and operational strategies proven effective across low-bandwidth deployments.
What this guide covers:
- Why big meetings fail in low-bandwidth regions (technical analysis)
- Core architecture requirements for reliable large-scale meetings
- Platform feature checklist for connectivity-constrained environments
- Operational preparation strategies for NGOs and governments
- Real-world case studies with documented outcomes
- Comparative platform analysis for low-bandwidth performance
Why Big Meetings Fail in Low-Bandwidth Regions
High Video Bitrate Without Optimization
Standard platforms default to HD video (720p-1080p) consuming 1.5-3 Mbps per stream. For participant viewing 5 active speakers simultaneously: 7.5-15 Mbps required. Rural 3G network providing 2 Mbps total? Connection fails immediately.
Platforms without adaptive bitrate streaming maintain quality until connection degrades catastrophically. No graceful degradation. Just frozen video and dropped participants.
Device CPU Throttling
Low-cost smartphones and older computers common in developing regions lack processing power for video decoding plus web app rendering plus encryption/decryption simultaneously.
Device CPU maxes out. Battery drains rapidly. Operating system throttles performance to prevent overheating. Video stutters. Audio lags. Eventually participant drops entirely—not from bandwidth but from device limitations.
Packet Loss on Rural Mobile Networks
Mobile networks in remote regions experience 5-15% packet loss routinely. Urban networks typically maintain <1% loss. This difference devastates real-time video:
1% packet loss: Minor quality degradation, barely noticeable
5% packet loss: Significant video artifacts, audio distortion
10% packet loss: Severe degradation, frequent reconnections
15% packet loss: Connection unsustainable, constant drops
Platforms without robust error correction and packet retransmission protocols fail at packet loss levels routine in developing regions.
Large Attendee Interactions Overloading Servers
1,000+ participant meetings generate enormous signaling traffic:
- Presence updates (who’s online/offline/away)
- Audio/video stream negotiations
- Chat messages propagating to all participants
- Reactions and hand-raises
- Polling responses
- Q&A submissions
Poorly architected platforms broadcast every interaction to every participant. 3,000 participants × 100 interactions/minute = 300,000 messages/minute requiring processing and transmission. Overwhelms both servers and client connections.
Lack of Adaptive Quality
Fixed-quality platforms assume connectivity matches requirements. When it doesn’t, they fail rather than adapt.
Adaptive platforms detect bandwidth constraints and automatically:
- Reduce video resolution
- Lower frame rates
- Compress audio
- Switch to audio-only mode
- Disable video entirely if necessary
Result: Degraded quality but maintained connection. For critical briefings, audio-only with slides is infinitely preferable to no connection.
Slow-Loading UI on Older Devices
Modern web applications load 3-5MB JavaScript frameworks before displaying interface. On 2G connection: 2-3 minute load time. On older device with limited RAM: another minute rendering.
Five minutes before participant even sees meeting interface. Many give up during loading, never actually joining.
Real Example: Humanitarian NGO in Rural Kenya
International NGO attempted 3,000-person emergency response training. Participants across rural Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania. Platform: Zoom Events purchased specifically for this training.
Results after 10 minutes:
- Started: 2,800 registered participants
- Actually joined successfully: 1,400 (50% failed to connect)
- Remained connected after 10 minutes: 680 (76% dropped)
- Completed full 90-minute session: 280 (90% attrition)
Post-event analysis:
- 60% of connection failures: Bandwidth insufficient for platform’s minimum requirements
- 25% of failures: Device CPU overload from video decoding
- 15% of failures: Packet loss causing repeated reconnection failures
Outcome: Training objectives completely failed. $40,000 platform investment wasted. Backup plan (regional in-person trainings) required three additional months and $120,000.
Understanding Bandwidth Constraints in Remote Regions
Typical Connectivity Conditions
2G Networks (EDGE):
- Theoretical maximum: 384 kbps
- Actual sustained throughput: 100-200 kbps
- Latency: 300-1000ms
- Packet loss: 5-15%
- Coverage: Still common in remote Africa, Asia, Pacific
3G Networks (HSPA):
- Theoretical maximum: 7-14 Mbps
- Actual sustained throughput: 1-3 Mbps
- Latency: 100-500ms
- Packet loss: 3-10%
- Coverage: Standard in developing region urban areas
Shared Community Networks:
- 10-50 households sharing single connection
- Effective per-user bandwidth: 500 kbps to 2 Mbps
- Highly variable based on concurrent usage
- Peak congestion during evenings
Congested Urban Slums:
- Hundreds of users per cell tower
- Bandwidth contention extreme during business hours
- Effective throughput often worse than rural 3G
- Frequent tower overload causing connection drops
Satellite Networks:
- Available bandwidth: 512 kbps to 5 Mbps
- Latency: 600-1000ms (geosynchronous orbit)
- Expensive per-GB pricing
- Weather-dependent reliability
Power Instability Affecting Infrastructure:
- Mobile towers on limited generator backup
- Frequent power outages degrading service
- Network equipment cycling creates connection instability
- Battery-powered devices prioritize connectivity over quality
Why Standard Webinar Platforms Struggle
Fixed Bitrate Streaming:
Zoom, Teams, Webex designed for corporate networks with 10+ Mbps reliable connectivity. Minimum bandwidth requirements:
- Zoom: 1.5 Mbps for group video
- Teams: 1.2 Mbps minimum
- Webex: 1.5-2 Mbps for video
These minimums exceed available bandwidth in many developing regions. No graceful degradation—connection simply fails.
Heavy UI Scripts:
Modern single-page applications load 3-5MB of JavaScript. Required for rich features in corporate environments. Disaster for 2G connections where loading takes minutes and consumes limited data allowances.
Lack of Offline Tolerance:
Brief connectivity interruptions (common on mobile networks) cause complete disconnection requiring full rejoin process. No session persistence. No automatic reconnection with context preservation.
Server-Side Processing in Distant Regions:
Major platforms route traffic through US or European data centers. Participant in Nairobi connecting to Virginia server:
- Physical distance: 11,000+ km
- Network hops: 15-25 routers
- Latency: 300-600ms
- Packet loss accumulation: 3-8%
Each hop degrades connection quality. Distance multiplies failure probability.
Core Technical Requirements for Running Big Meetings on Low Bandwidth
1. Adaptive Video Quality (Per-User Optimization)
Essential Capability:
Platform must automatically adjust video quality for each participant based on their individual connection:
Connection Quality Detected → Automatic Response:
Excellent (>5 Mbps): HD video, 30 fps, full quality
Good (2-5 Mbps): SD video, 15-24 fps, compressed
Fair (1-2 Mbps): Low-res video, 10-15 fps, high compression
Poor (500 kbps-1 Mbps): Audio + slides only, minimal video
Very Poor (<500 kbps): Audio-only mode, text chat
Dynamic Adjustment:
Connection quality fluctuates. Participant starts meeting on WiFi, switches to mobile, moves to area with poor coverage. Platform must adapt continuously without dropping connection.
Convay Implementation:
Participants automatically transition between quality levels seamlessly. 3G connection degrades? Video reduces to audio-plus-slides without disconnection. Connection improves? Quality upgrades automatically. Participant never manually configures—intelligence is built-in.
Measurable Impact:
NGO comparing Zoom vs Convay in same low-bandwidth environment:
- Zoom: 45% connection success rate (participants completing session)
- Convay: 94% connection success rate
- Difference: 109% improvement in successful participation
2. Distributed Architecture & Geo-Edge Routing
Why This Matters:
Geographic distance directly impacts connection quality:
Nairobi → Virginia (11,000 km):
- Latency: 350ms minimum
- Packet loss: 4-7%
- Bandwidth overhead: 15-20%
Nairobi → Regional Node (500 km):
- Latency: 50-80ms
- Packet loss: 1-2%
- Bandwidth overhead: 5-8%
Architecture Requirement:
Platform must deploy regional infrastructure so participants connect to geographically-nearest servers. Reduces:
- Round-trip latency (better interactivity)
- Packet loss (fewer connection failures)
- Bandwidth requirements (reduced overhead)
- Dependency on international backbone (avoids choke points)
Major Platform Limitations:
Zoom and Webex route most traffic through US/EU data centers even when all participants are in Africa or Asia. Architecture optimized for North American corporate customers, not global humanitarian operations.
Sovereign Deployment Advantage:
On-premise or national cloud deployment means meeting traffic never leaves region. Government in Bangladesh hosting meeting for Bangladeshi participants? All traffic stays within Bangladesh. Zero international routing. Optimal performance.
3. Server-Side Media Mixing
Technical Explanation:
Client-Side Processing (Standard Platforms):
Each participant’s device receives individual video streams from every active speaker:
- 5 speakers sharing video simultaneously
- Each participant downloads 5 separate streams
- Device CPU decodes 5 videos
- Bandwidth: 5 × 1.5 Mbps = 7.5 Mbps required
- CPU usage: High (multiple decode operations)
Server-Side Processing (Optimized Platforms):
Server combines all speaker videos into single mixed stream:
- 5 speakers sharing video simultaneously
- Server mixes into single output
- Each participant downloads 1 stream only
- Bandwidth: 1.5 Mbps total
- CPU usage: Low (single decode operation)
Impact on Low-Bandwidth Scenarios:
Server-side mixing enables meeting participation on connections and devices that otherwise fail:
- 80% reduction in bandwidth requirements
- 75% reduction in device CPU usage
- Supports older smartphones and low-cost devices
- Enables participation on 2G/3G networks
Especially Critical for Large Meetings:
1,000+ participant meetings with 10+ active speakers simultaneously. Without server-side mixing: Impossible on low-bandwidth connections. With mixing: Feasible on 3G.
4. Bandwidth-Adaptive AI Features
The Problem:
AI features—transcription, translation, recording, summaries—add computational and bandwidth overhead. Implemented poorly, they make connection requirements even higher.
Poor Implementation:
- Audio streams to cloud AI service for transcription (doubles bandwidth)
- Translation requires separate data channels (adds 20-30% overhead)
- Real-time captioning downloads compete with video (unstable on limited bandwidth)
Optimized Implementation:
Server-Side AI Processing:
AI runs on meeting infrastructure, not participant devices or external services:
- Audio/video stays within meeting server cluster
- AI inference occurs server-side
- Only results (text transcripts, translations) send to participants
- Minimal bandwidth impact—text vs video/audio
Bandwidth-Conscious Delivery:
Transcripts and translations delivered using text-only channels requiring <10 kbps. Even on severely bandwidth-constrained connections, captions remain functional.
Convay Approach:
AI transcription (Bengali, English) and translation run on meeting servers. Participants receive text captions using minimal bandwidth. Audio never leaves meeting infrastructure for external AI processing. Result: AI features work even on 2G connections where other platforms disable AI to preserve connectivity.
5. Efficient Codec Support
Why Codecs Matter:
Codec = compression algorithm determining how much bandwidth video/audio requires at given quality level.
Modern Efficient Codecs:
VP9 (Video):
- 30-50% more efficient than H.264
- Same quality at half the bandwidth
- Widely supported in modern browsers
AV1 (Video):
- 30-40% more efficient than VP9
- Cutting-edge compression
- Limited browser support currently
Opus (Audio):
- Superior clarity at low bitrates
- Excellent performance 16-32 kbps range
- Resilient to packet loss
- Ideal for speech in meetings
Automatic Codec Degradation:
Platform must support fallback to ultra-low-bitrate modes:
- 32 kbps audio (speech quality sufficient for meetings)
- 16 kbps audio (intelligible in emergencies)
- Text-based communication as absolute fallback
Practical Impact:
Meeting requiring 1.5 Mbps with H.264 video can run on 800 kbps with VP9, or 500 kbps audio-only with Opus. Difference between inaccessible and functional in low-bandwidth regions.
6. Low-Latency Reconnect & Error Recovery
The Challenge:
Mobile networks in developing regions don’t maintain stable connections. Brief interruptions happen constantly:
- Tower handoffs between cells
- Temporary congestion
- Brief power fluctuations
- Network equipment cycling
Each interruption can disconnect participants if platform lacks robust recovery.
Essential Recovery Features:
Automatic Reconnection:
- Connection drops detected within 2-3 seconds
- Reconnection attempt automatic, no user action required
- Multiple retry strategies (exponential backoff)
- Success rate >95% for temporary disconnections
Packet Retransmission:
- Lost packets detected and retransmitted
- Prevents quality degradation from normal packet loss
- Critical for mobile networks with 5-10% loss
Jitter Buffering:
- Compensates for variable latency
- Smooths audio/video playback
- Prevents stuttering from inconsistent packet arrival
Bandwidth Prediction:
- Platform learns connection patterns
- Proactively adjusts quality before degradation
- Reduces disruptive quality transitions
Session Persistence:
- Brief disconnections don’t end session
- Participant rejoins at same point
- Chat history, shared content, meeting state preserved
- Feels like temporary pause, not disconnection
Measured Results:
Platform comparison in rural Uganda (1,500 participants, 90-minute meeting):
Without Advanced Recovery (Zoom):
- 670 disconnection events
- 280 participants dropped permanently (19% lost)
- Average 3.2 disconnections per participant who completed
With Advanced Recovery (Convay):
- 630 disconnection events (similar network conditions)
- 45 participants dropped permanently (3% lost)
- Average 0.8 disconnections noticed by participants
- Improvement: 533% better retention despite similar network conditions
Platform Feature Checklist for Large Meetings in Low Bandwidth Regions
Must-Have Technical Features
Audio-First Fallback:
- ✅ Automatic downgrade to audio when video unsustainable
- ✅ Audio-only join option for participants anticipating connectivity issues
- ✅ Seamless transition between video and audio modes
- ✅ Audio-with-slides mode (minimal bandwidth, effective communication)
Single-Stream Delivery:
- ✅ Server-side mixing eliminates multiple stream downloads
- ✅ Reduces bandwidth 60-80% in multi-speaker scenarios
- ✅ Reduces device CPU load enabling older hardware participation
Adaptive Bitrate:
- ✅ Per-participant automatic quality adjustment
- ✅ Dynamic response to changing connectivity
- ✅ Granular quality levels (not just HD/SD binary)
- ✅ Bandwidth prediction to prevent disruptive transitions
Low-Latency Signaling:
- ✅ Fast reconnection (< 5 seconds typical)
- ✅ Minimal overhead for presence and interaction
- ✅ Efficient chat and reaction propagation
- ✅ Optimized polling and Q&A data structures
Region-Aware Server Routing:
- ✅ Participants connect to geographically nearest infrastructure
- ✅ Minimizes international backbone dependency
- ✅ Reduces latency, packet loss, jitter
- ✅ Sovereign/regional deployment options
Lightweight Front-End Rendering:
- ✅ Fast loading (< 500KB initial download)
- ✅ Progressive enhancement (core features first, enhancements optional)
- ✅ Efficient DOM manipulation (works on older browsers)
- ✅ Minimal memory footprint (< 100MB typical)
Transcript-Only Mode:
- ✅ Text-based participation when audio/video fail
- ✅ Minimal bandwidth (< 10 kbps)
- ✅ Accessible on any connection
- ✅ Useful for follow-along when audio quality poor
SMS or Lightweight Join:
- ✅ SMS notifications with simple join links
- ✅ Progressive web app (no install required)
- ✅ Works on feature phones (basic models)
- ✅ Fallback to telephone dial-in
Must-Have Admin Features
Moderator Bandwidth Controls:
- ✅ Ability to force participants to audio-only mode
- ✅ Disable participant video uploads globally
- ✅ Adjust quality tiers for entire meeting
- ✅ Priority bandwidth allocation for presenters
Bulk Mute & Control:
- ✅ Mute all participants (reduces server load)
- ✅ Disable video for all (improves connection stability)
- ✅ Lock settings to prevent participant override
- ✅ Graduated permission system
Dynamic Spotlighting:
- ✅ Highlight active speaker only
- ✅ Reduces streams participants must decode
- ✅ Conserves bandwidth by focusing attention
- ✅ Automatic speaker detection
Simplified Participant UI:
- ✅ Hide non-essential features for low-bandwidth users
- ✅ Reduce visual complexity
- ✅ Minimize JavaScript execution
- ✅ Lightweight mode option
How NGOs and Governments Can Prepare for Big Meetings in Weak Connectivity Zones
1. Pre-Event Bandwidth Assessment
Conduct Diagnostic Testing:
Two weeks before major event, survey participant connectivity:
- Simple speed test link distributed via email/SMS
- Collects: download speed, upload speed, latency, packet loss
- Aggregated data shows connectivity distribution
Example Results:
1,000 expected participants pre-tested:
- 15% have >5 Mbps (excellent)
- 30% have 2-5 Mbps (good)
- 35% have 1-2 Mbps (fair)
- 15% have 500 kbps-1 Mbps (poor)
- 5% have <500 kbps (very poor)
Planning Implications:
55% of participants require adaptive quality or audio-focused delivery. Platform must handle this gracefully. Event strategy should emphasize audio and slides over video-heavy presentations.
2. Provide Low-Bandwidth Join Instructions
Create Participant Guide:
“Joining from Low-Bandwidth Location” instructions:
For Mobile Users:
- Use audio-only mode (instructions with screenshots)
- Disable HD video in settings
- Close other apps consuming bandwidth
- Connect to WiFi if available (but 3G works too)
For Computer Users:
- Use Chrome/Firefox (efficient video decoding)
- Close unnecessary browser tabs
- Disable automatic video in preferences
- Use wired connection if available
Emergency Fallback:
- Telephone dial-in number provided
- Audio-only + slides follow-along option
- Transcript distributed post-meeting
Language Accessibility:
Translate instructions into local languages. English-only instructions create barriers for participants whose native language differs.
3. Reduce Visual Load
Presentation Design for Low Bandwidth:
Avoid:
- ❌ HD video clips embedded in presentations
- ❌ Animated transitions between slides
- ❌ Rapid slide changes (> 1 per 10 seconds)
- ❌ Video backgrounds or virtual sets
- ❌ Multiple presenters with video simultaneously
Prefer:
- ✅ Static slides with clear text
- ✅ Simple graphics and charts
- ✅ Single speaker video focus
- ✅ Slide changes minimized (substantial content per slide)
- ✅ Audio-primary delivery with slides supporting
Content Distribution:
Send slide deck to participants 24 hours before meeting. They can follow along locally even if screen sharing fails. Reduces dependency on perfect connectivity.
4. Have a Fallback Channel
Multi-Channel Strategy:
Primary: Video meeting platform
Backup: Audio-only telephone conference bridge
Tertiary: WhatsApp group for text updates
Asynchronous: Email distribution of recording and transcript
Real-Time Backup:
If video meeting fails catastrophically, immediate pivot to telephone conference. Participants receive SMS with dial-in number. Meeting continues audio-only while platform issue resolves.
Post-Meeting Access:
Not all participants successfully join live session despite best efforts. Provide:
- Recording with transcript (multiple languages if multilingual audience)
- Key points summary document
- Q&A compilation
- Follow-up materials
Ensures information reaches everyone even if connectivity prevented live participation.
How Large Meetings (3,000-10,000 Attendees) Can Still Work in Remote Regions
Polling, Q&A & Translation Optimization
Efficient Interactive Features:
Polling (3,000+ participants):
Poor implementation:
- Each vote broadcasts to all participants
- 3,000 votes = 9 million messages (3,000 × 3,000)
- Server overload, client overload, connection failures
Optimized implementation:
- Votes send to server only
- Server aggregates results
- Only final results broadcast to participants
- Bandwidth: 99.9% reduction
Q&A (3,000+ participants):
Poor implementation:
- All questions visible to all participants immediately
- Constant UI updates
- High data consumption
Optimized implementation:
- Questions submit to moderation queue
- Approved questions display
- Batched UI updates (every 5 seconds vs real-time)
- Bandwidth: 95% reduction
Translation:
Poor implementation:
- Every message translates individually
- Multiple round-trips to translation service
- High latency, high bandwidth
Optimized implementation:
- Translation caching (common phrases)
- Batch processing
- Local translation for common language pairs
- Bandwidth: 70% reduction
Convay Architecture:
Server-side aggregation and batched updates standard. Interactive features designed for 10,000+ participants on varied connectivity. Tested extensively in low-bandwidth environments.
Case Study: 5,200-Person Government Training in Rural Region
Organization: National government ministry
Event: Mandatory training for provincial officials
Participants: 5,200 attendees across rural provinces
Platform: Convay Big Meetings
Connectivity: 40% of participants on <1 Mbps connections
Technical Approach:
Pre-Event:
- Bandwidth assessment (2 weeks prior)
- Distributed low-bandwidth join guide (local language)
- Pre-loaded slide deck to participant devices
- Telephone backup numbers distributed
During Event:
- Automatic quality adaptation enabled
- 68% of participants fell back to audio-primary mode
- Server-side mixing reduced bandwidth requirements
- Regional server deployment (all traffic within country)
Results:
Participation:
- 5,200 registered
- 4,920 joined successfully (95% connection rate)
- 4,740 remained connected full session (91% retention)
- 95% participant retention throughout 2-hour program
Quality:
- Zero major outages
- Average connection quality rating: 7.8/10 (participant survey)
- 88% reported audio clarity “good” or “excellent”
- AI Bengali captions functional for 92% of session
Comparison to Previous Attempt:
Ministry previously attempted similar training using Zoom Events:
- 4,200 registered
- 2,100 joined successfully (50% connection rate)
- 980 remained connected full session (23% retention)
Improvement with Convay:
- 90% improvement in successful joins
- 384% improvement in session retention
- Training objectives actually achieved
Case Study: NGO Field Coordinators Across 12 Countries
Organization: International humanitarian NGO
Event: Monthly coordination call
Participants: 380 field staff across Sub-Saharan Africa
Platform: Convay (switched from Zoom after repeated failures)
Connectivity: Majority on 3G mobile, some 2G/EDGE
Challenge:
Previous platform (Zoom) experienced 40-60% dropout rate. Field staff reported frustration, missed critical information, coordination suffered.
Convay Implementation:
Technical Configuration:
- Audio-first mode default
- Single-stream delivery enabled
- Automatic reconnection aggressive (5 retry attempts)
- Regional server deployment (Africa-based infrastructure)
Operational Changes:
- Reduced presentation complexity
- Audio-focused delivery (slides secondary)
- Telephone dial-in backup
- WhatsApp group for critical updates
Results:
Connectivity Success:
- 380 participants
- 372 connected successfully (98% success rate)
- 364 remained connected full session (96% retention)
- Average 0.3 disconnections per participant (vs 2.7 with Zoom)
Bandwidth Savings:
- Single-stream mode saved estimated 60% bandwidth vs multi-stream
- Audio-first fallback enabled participation on connections that would fail video-first platforms
- Regional routing reduced latency 300ms → 80ms average
Organizational Impact:
- Meeting consistency improved (reliable monthly cadence)
- Staff satisfaction increased (technology finally worked)
- Coordination effectiveness measurably better
- NGO saved $18,000 annually in platform costs (Convay less expensive + eliminated need for regional in-person gatherings compensating for technology failures)
Comparison Table: Big Meeting Performance in Low-Bandwidth Regions
| Feature | Convay | Zoom | Webex | Teams |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Audio-First Fallback | ✅ Automatic | ⚠️ Limited | ⚠️ Limited | ❌ No |
| Adaptive Bandwidth | ✅ Advanced | ⚠️ Moderate | ⚠️ Moderate | ⚠️ Weak |
| Edge Routing | ✅ Strong | ⚠️ Weak | ⚠️ Regional | ⚠️ Weak |
| Low-Power Device Support | ✅ Excellent | ⚠️ Moderate | ⚠️ Weak | ⚠️ Weak |
| 3G/2G Reliability | ✅ High | ❌ Low | ❌ Low | ❌ Low |
| Server-Side Mixing | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ⚠️ Limited | ❌ No |
| Supports 5K-10K Attendees | ✅ Yes | ✅ Paid tiers | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Minimum Bandwidth | 🟢 200 kbps | 🟡 1.5 Mbps | 🟡 1.5 Mbps | 🟡 1.2 Mbps |
| Reconnection Speed | 🟢 < 5 sec | 🟡 15-30 sec | 🟡 10-20 sec | 🟡 15-30 sec |
| Packet Loss Tolerance | 🟢 15% | 🔴 5% | 🟡 8% | 🔴 5% |
| Regional Deployment | ✅ Full | ❌ Limited | ⚠️ Some | ❌ Limited |
| Best For | NGOs, Gov, Rural Ops | Corporate, Urban | Cisco Shops | Internal HR |
| Cost at 5K Scale | $34,800/year | $24,900+ | $35,000+ | Not suitable |
Key Takeaway:
Convay architecturally designed for low-bandwidth environments. Other platforms designed for corporate high-bandwidth networks with limited accommodation for connectivity constraints.
Best Practices for Sustaining Meeting Quality Across Remote Regions
Minimize Presenter Motion
Why It Matters:
Video compression algorithms work by detecting what changed between frames. More motion = more changes = more data to transmit.
Presenter sitting relatively still: 200-400 kbps
Presenter moving frequently: 800-1200 kbps
Difference: 3x bandwidth for same video quality
Practical Application:
Brief presenters: Minimize gesticulation, avoid pacing, sit rather than stand when possible. Not about restricting expression—about recognizing technical constraints.
Use Audio-Based Delivery for Critical Briefings
Reality Check:
When connectivity constrained, audio clarity matters more than video quality. Human voice carries meaning effectively. Video adds relatively little when content is information-dense.
Strategy:
Critical briefings (emergency response, policy updates, operational instructions): Optimize for audio clarity. Video optional. Slides supporting. Ensure audio remains intelligible even if video fails.
Disable Attendee Video Globally
Large Meeting Reality:
3,000 participant meeting where everyone enables video: Platform must process 3,000 incoming video streams even if only displaying 10-20. Enormous server load. Unnecessary bandwidth consumption.
Best Practice:
Host and presenters: Video enabled
Participants: Video disabled, audio-only by default
Exception: Small breakout groups where interaction benefits from video
Impact:
Bandwidth requirements drop 80-90%. Server load decreases proportionally. Connection stability increases dramatically. Meeting experience improves for everyone.
Keep Slides Lightweight
File Size Targets:
Total presentation: < 10MB
Individual slide: < 500KB
Embedded images: < 200KB each, compressed
Avoid:
- High-resolution photos (1MB+ each)
- Embedded videos
- Complex animations
- Gradient backgrounds (compress poorly)
Prefer:
- Simple graphics
- Vector images where possible
- Solid color backgrounds
- Text-focused slides
Record Server-Side Only
Client-Side Recording Issues:
When participants record locally:
- Increased device CPU usage
- Potential bandwidth impact
- Quality varies by device capability
- Multiple unauthorized recordings
Server-Side Recording Benefits:
- No participant device impact
- Consistent quality
- Centralized control
- Easier distribution
- Supports post-meeting editing
Provide Transcript After Session
Accessibility and Catch-Up:
Participants who couldn’t join, experienced connection issues, or need reference material benefit from transcript availability.
Multi-Language Translation:
For multilingual audiences, translate transcript into relevant languages. Expands accessibility beyond live interpretation limitations.
Use Regional Servers or Sovereign Cloud
Geographic Proximity Impact:
International Routing:
- Nairobi → Virginia: 350ms latency, 5% packet loss
- Connection quality: Fair to poor
Regional Routing:
- Nairobi → Nairobi: 20ms latency, 1% packet loss
- Connection quality: Good to excellent
Sovereign Deployment Advantages:
Government hosting meeting for domestic participants? On-premise or national cloud deployment means:
- All traffic stays within country
- Optimal routing (national backbone)
- No international bandwidth costs
- Improved reliability
- Compliance with data residency requirements
Why Sovereign or Local Hosting Improves Low-Bandwidth Performance
The Foreign Cloud Routing Problem
Architectural Issue:
Major platforms (Zoom, Teams, Webex) route traffic through centralized data centers optimized for North American and European markets. Even when all meeting participants are in Africa or Asia, data often routes through US or Europe.
Concrete Example:
Meeting in Bangladesh with 100% Bangladeshi participants using Zoom:
- Participant in Dhaka sends video
- Video routes to Zoom server in Singapore or Mumbai
- Server processes and distributes
- Video returns to other Dhaka participants
- Result: Thousands of kilometers unnecessary routing
Impact:
- Added latency: +150-300ms
- Added packet loss: +2-5%
- International bandwidth consumption
- Dependency on submarine cable capacity
- Failure points multiplied
Local Hosting Advantages
Optimal Routing:
Meeting in Bangladesh using Convay deployed on national infrastructure:
- Participant in Dhaka sends video
- Video routes to server in Dhaka (50km)
- Server processes and distributes
- Video delivers to other Dhaka participants (50km)
- Result: 100km total vs 10,000km with foreign cloud
Measured Improvements:
Latency:
- Foreign cloud: 250-400ms typical
- Local hosting: 30-80ms typical
- Improvement: 70-85% latency reduction
Packet Loss:
- Foreign cloud: 4-8% typical
- Local hosting: 1-2% typical
- Improvement: 60-75% packet loss reduction
Bandwidth:
- Foreign cloud: 2-3 Mbps required for HD
- Local hosting: 1.2-1.8 Mbps for same quality
- Improvement: 40-50% bandwidth efficiency
Regional Optimization
African Example:
Meeting connecting participants across Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda using regional server deployment:
- All traffic routes through Africa
- No unnecessary international transit
- Consistent performance across countries
- Reduced cost (no international bandwidth charges)
Versus foreign cloud:
- Traffic routes to Europe or US
- Multiple international cable transits
- Variable performance (depends on international backbone)
- Higher cost (international bandwidth premium)
Critical for Government and NGOs
Organizations working in developing regions benefit most from regional/local deployment:
Government: Data sovereignty requirements often mandate local hosting anyway. Performance improvement bonus on top of compliance necessity.
NGOs: Operating across multiple low-connectivity countries. Regional deployment provides consistent experience unavailable from centralized foreign clouds.
Development Organizations: Cost sensitivity combined with reach requirements. Local hosting reduces bandwidth costs while improving reliability.
Final Takeaway: Scalable Meetings Require Smart Architecture, Not More Bandwidth
The Fundamental Truth
You don’t need high-speed internet to run high-impact webinars. You need platforms engineered for low-bandwidth regions, large audiences, and real-world constraints.
What Matters More Than Raw Bandwidth
Adaptive Intelligence: Platform that adjusts to available connectivity rather than demanding fixed requirements
Efficient Architecture: Server-side mixing, regional deployment, optimized codecs reduce bandwidth needs 60-80%
Robust Recovery: Automatic reconnection and error correction compensate for unstable networks
Operational Design: Audio-first delivery, lightweight slides, simplified UI work within constraints
Geographic Proximity: Local/regional hosting eliminates unnecessary routing inefficiencies
The Infrastructure Investment Trade-Off
Organizations face choice:
Option A: Wait for connectivity infrastructure to improve
Timeline: 5-10 years for widespread high-bandwidth in remote regions
Cost: Trillions in telecommunications infrastructure investment
Certainty: Low (market-dependent, political, economic factors)
Option B: Use platforms designed for current connectivity reality
Timeline: Immediate
Cost: Platform selection and minor operational adaptation
Certainty: High (proven technology, documented results)
Most organizations cannot wait for perfect infrastructure. They need solutions working with today’s connectivity, not tomorrow’s aspirational networks.
Convay’s Low-Bandwidth Design Philosophy
Purpose-built for organizations operating in challenging environments:
Geographic Focus: Bangladesh, MENA, Africa, South Asia, Pacific—regions where connectivity constraints are daily reality, not edge case.
Architecture Decisions: Every feature evaluated through lens: “Does this work on 3G mobile in rural setting?” If no, redesign or eliminate.
Measured Performance: Real-world testing across developing regions. Not simulated lab conditions, actual field deployments with actual connectivity constraints.
Result: Platform where 95%+ connection success rates in low-bandwidth environments is standard, not exceptional. Where 3,000-person meetings run reliably on infrastructure that defeats other platforms.
Because for NGOs coordinating humanitarian response, governments conducting rural development training, health organizations deploying vaccination campaigns—technology either works in field conditions or it doesn’t matter how well it works in Silicon Valley.
Frequently Asked Questions
Large meetings fail primarily because platforms are optimized for urban high-speed networks. High video bitrate, non-adaptive streaming, CPU-heavy clients, and long routing paths cause freezes, drops, and complete disconnections.
2G networks deliver 100–200 kbps and 3G networks typically provide 1–3 Mbps. Latency ranges 100–1000ms with 5–15% packet loss—far below what standard webinar tools require.
Convay uses server-side media mixing, adaptive bitrate streaming, geo-edge routing, and low-latency error recovery. These dramatically reduce bandwidth and processing load for each participant.
Instead of downloading 5–10 video streams, users receive one combined stream. This reduces bandwidth by 60–80% and CPU usage by 70–75%, allowing participation even on weak mobile devices.
Adaptive quality automatically lowers resolution, frame rates, and even switches to audio-only mode based on user connectivity—preventing disconnections and frozen screens.
They use fixed bitrate streaming, heavy UI frameworks, and route traffic through distant US/EU servers. These require more bandwidth and processing than most rural/urban-slum networks can provide.
Convay includes packet retransmission, jitter buffering, and bandwidth prediction to smooth real-time communication even with 10–15% packet loss—conditions where other platforms fail.
Yes. Convay’s lightweight client, single-stream delivery, and low CPU decoding requirements allow smooth participation on low-cost smartphones and older laptops.
Yes. Convay automatically switches users to audio-only or transcript-only modes when needed, ensuring continuous participation even below 500 kbps bandwidth.
Run connectivity diagnostics, provide low-bandwidth joining instructions, simplify slides, reduce video load, and create fallback channels like audio-only or WhatsApp text updates.